July Inflation has been one of the most closely watched economic indicators in recent years, especially in the wake of the pandemic and its aftermath. With July’s inflation data coming in line with expectations, investors are now turning their attention to the possibility of interest rate cuts in the near future. But what does this mean for the economy, the market, and the average investor? In this blog, we’ll delve into the key aspects of July inflation, its current trajectory, and the potential implications of future rate cuts.
Understanding Inflation and Its Impacts
What is Inflation?
Inflation refers to the general increase in prices of goods and services over time, which erodes the purchasing power of money. It’s a natural part of economic cycles, but the rate at which it occurs can have significant implications for both consumers and the broader economy.
There are several causes of July inflation, including increased demand for products and services, rising production costs, and expansive monetary policies. Central banks, like the Federal Reserve, monitor inflation closely as part of their mandate to ensure price stability and full employment.
Historical Context: Inflation Trends Post-Pandemic
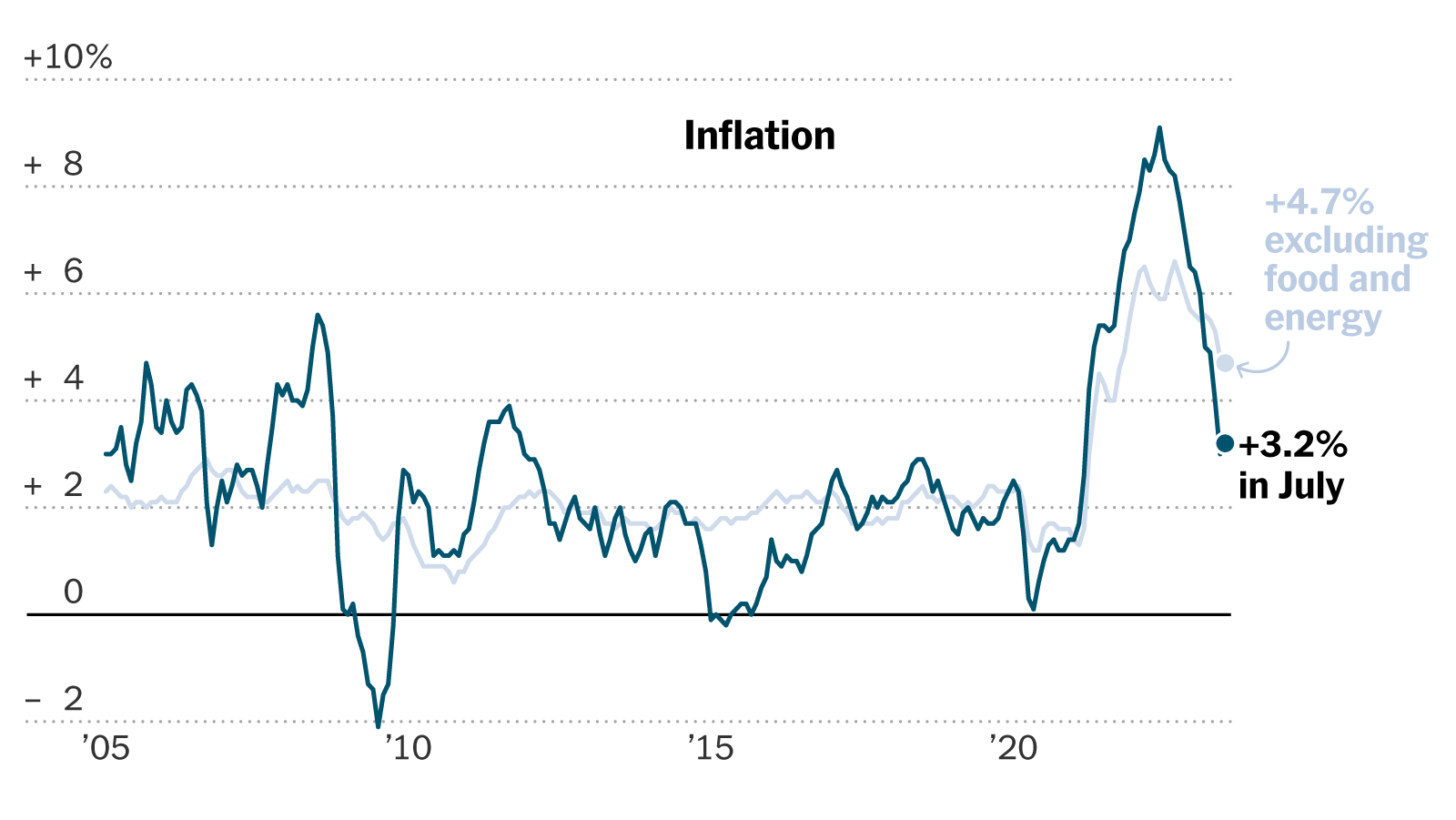
The COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented disruptions to the global economy, leading to sharp contractions in economic activity and massive government spending to support households and businesses. As economies began to recover, supply chain disruptions and labor shortages led to an acceleration in July inflation, reaching levels not seen in decades.
In 2021 and 2022, inflation soared as the economy rebounded. The Federal Reserve responded by raising interest rates aggressively to curb rising prices. However, by mid-2023, July inflation began to moderate, leading to cautious optimism among policymakers and investors that the worst might be over.
2. July’s Inflation Data: A Closer Look
Key Takeaways from the July Inflation Report
The July inflation report was closely monitored by analysts and investors alike. According to the data released, inflation was in line with market expectations, suggesting that the measures taken by the Federal Reserve to control price increases were beginning to take effect.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the average change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services, showed a moderate increase. The year-over-year July inflation rate for July was reported at 3.2%, slightly below June’s figure, indicating a stabilization in price pressures.
Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, remained steady, suggesting that underlying inflationary pressures were not accelerating. This data was welcomed by the market, as it reinforced the view that the Fed’s rate hikes were successfully containing inflation.
Comparison with Previous Months
When compared to the earlier months of 2023, the July inflation data continued the trend of gradual deceleration in price growth. This moderation in inflation was consistent with the Fed’s forecasts and aligned with their goal of bringing inflation back down to their target range of 2%.
The key contributors to inflation in July were housing, food, and energy prices. While energy prices saw some volatility, housing costs remained elevated, driven by a tight supply of homes and rising rents. Food prices also saw a modest increase, though at a slower pace than earlier in the year.
3. Market Reactions and Investor Sentiment
How the Market is Responding
The market’s response to the July inflation data was largely positive. With inflation figures aligning with expectations, there was a sense of relief among investors that the Fed might not need to pursue further aggressive rate hikes. This optimism was reflected in the stock market, with major indices posting gains following the release of the report.
Bond markets also reacted to the inflation data. The yield on the 10-year Treasury note, a key benchmark for interest rates, remained stable, suggesting that investors were not anticipating significant changes in the Fed’s policy direction in the near term.
Investor Sentiment: Are Rate Cuts on the Horizon?
Investor sentiment is now increasingly focused on the possibility of rate cuts. As July inflation moderates and economic growth slows, there is growing speculation that the Fed could pivot to cutting rates in 2024 to support the economy.
However, the timing and extent of any potential rate cuts remain uncertain. The Fed has emphasized that its decisions will be data-dependent, and much will depend on how inflation and economic growth evolve in the coming months.
4. Potential Rate Cuts: Implications and Predictions
Why Rate Cuts Matter
Interest rate cuts are significant because they can lower the cost of borrowing, stimulate economic activity, and support asset prices. For businesses, lower rates reduce the cost of capital, encouraging investment and expansion. For consumers, lower rates can make mortgages, car loans, and other forms of credit more affordable, boosting spending.
However, rate cuts can also have downsides. If implemented prematurely, they can reignite inflationary pressures, undermining the progress made in stabilizing prices. Moreover, lower rates can reduce returns on savings and fixed-income investments, posing challenges for retirees and conservative investors.

Possible Scenarios for Future Rate Cuts
The possibility of rate cuts hinges on several factors:
- Economic Growth: If economic growth continues to slow, the Fed might be compelled to cut rates to prevent a recession.
- Inflation Trajectory: A sustained decline in inflation would give the Fed more room to lower rates without risking a resurgence in price pressures.
- Labor Market Conditions: The strength of the labor market will also be crucial. A weakening job market could prompt the Fed to ease monetary policy to support employment.
Given these factors, some analysts predict that the Fed could start cutting rates as early as the first half of 2024, while others believe that rate cuts might not occur until later in the year or even 2025, depending on how economic conditions unfold.
5. What It Means for the Average Investor
Investment Strategies in a Low-Interest-Rate Environment
For investors, a low-interest-rate environment can present both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, lower rates can support stock prices, particularly in sectors like technology, real estate, and consumer discretionary, where growth prospects are closely tied to economic conditions. On the other hand, lower rates can reduce yields on bonds and savings accounts, leading to lower income for fixed-income investors.
To navigate this environment, investors might consider the following strategies:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes can help manage risk.
- Focus on Growth Stocks: Growth stocks tend to perform well in low-rate environments as they benefit from lower borrowing costs and higher consumer spending.
- Real Estate Investment: Real estate can offer protection against inflation and benefit from lower mortgage rates.
- Dividend-Paying Stocks: Companies with strong dividend track records can provide a steady income stream even when interest rates are low.
Risks and Opportunities
While the prospect of rate cuts might be appealing, it’s important for investors to remain vigilant about potential risks. These include:
- Market Volatility: Changes in interest rate expectations can lead to volatility in stock and bond markets.
- Inflation Risks: If inflation resurges, the Fed may be forced to raise rates again, which could negatively impact asset prices.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Geopolitical events, trade tensions, and other global factors can also influence market conditions and investor sentiment.
6. Conclusion
July’s inflation data, which came in line with expectations, has provided some reassurance to investors that the worst of the inflationary pressures may be behind us. However, the focus is now shifting to what the Federal Reserve will do next. With the possibility of rate cuts on the horizon, investors need to be prepared for a range of scenarios.
For the average investor, this means staying informed, being adaptable, and considering strategies that can thrive in a low-interest-rate environment. Diversification, a focus on growth and dividend-paying stocks, and an eye on real estate could help navigate the complexities of the current economic landscape.
As we look ahead, it’s clear that the interplay between inflation, interest rates, and economic growth will continue to be a dominant theme in the financial markets. By understanding these dynamics, investors can better position themselves to take advantage of the opportunities that lie ahead, while also mitigating potential risks.
Read more – click here








Leave a Reply